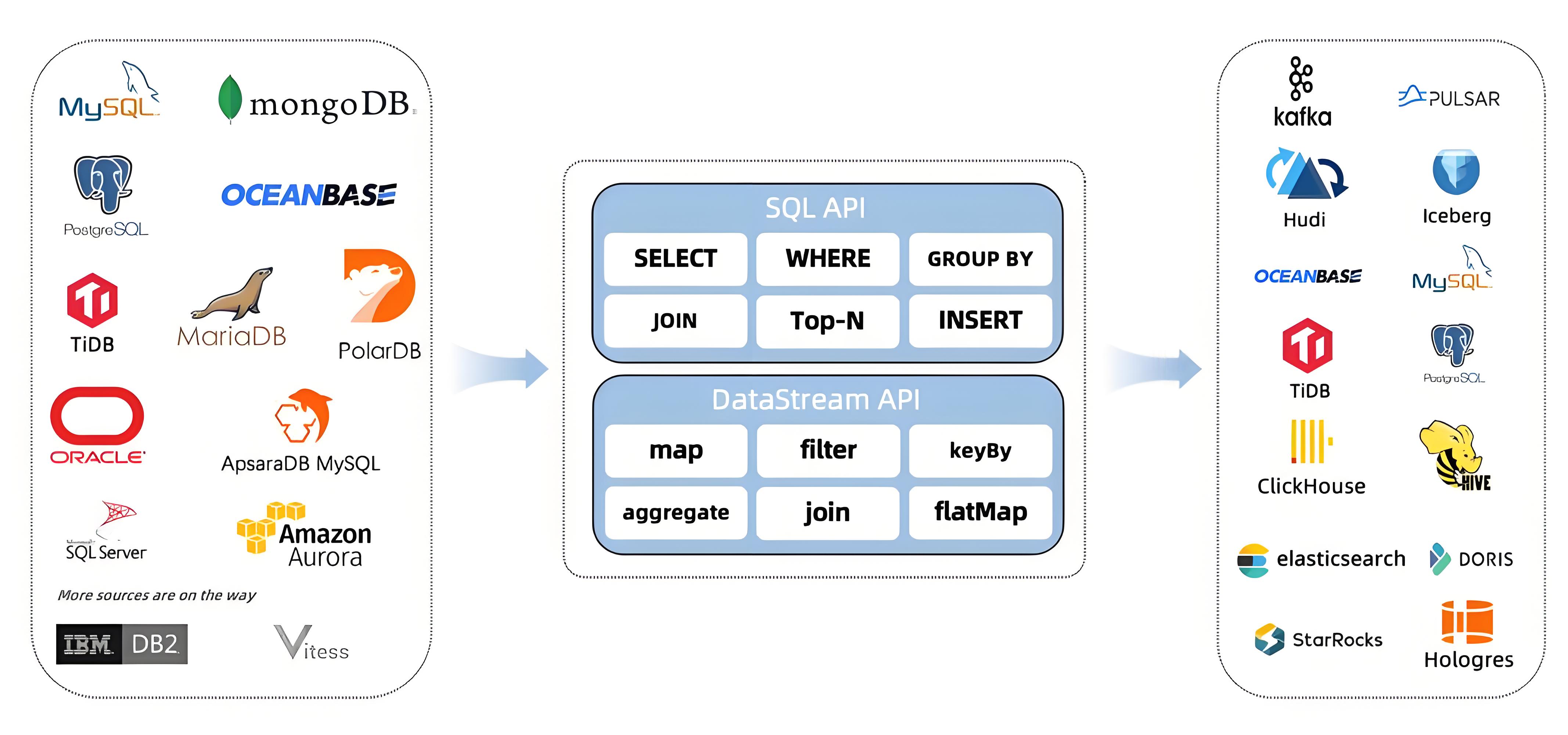
1、何为Flink CDC?
Flink CDC 是 Apache Flink 社区提供的一种数据捕获和同步的解决方案,它可以捕获数据库的变化数据并将其实时同步到其他存储系统中,如 Kafka、HBase 或其他数据库。Flink CDC 利用了 Debezium 来捕获数据库中的变化,并通过 Flink 的流式处理框架进行处理和传输。
1.1、Debezium 又是什么?
Debezium 是一个开源的分布式数据捕获(CDC, Change Data Capture)平台,它用于实时捕获数据库中的数据变更并将这些变更以事件的形式发布到数据流系统(例如 Kafka)中。Debezium 支持多种数据库,包括 MySQL、PostgreSQL、MongoDB、SQL Server 等,帮助开发者和企业实现高效的数据同步和数据集成。
1.1.1、Debezium 的工作原理
Debezium 的核心工作原理是基于数据库的 Write-Ahead Log (WAL) 或 binlog 日志。这些日志记录了数据库中的每一个插入、更新和删除操作。Debezium 通过读取这些日志文件来检测数据的变化,然后将这些变化作为事件(例如插入、更新或删除的事件)发送到 Kafka 等消息队列中,供下游的应用或服务进行消费。
1.1.2、Debezium 的核心功能
- 实时数据捕获:通过监控数据库的事务日志,Debezium 能够实时捕获所有的变更操作,包括插入、更新、删除等操作,并且无缝地将这些变更发送到下游系统。
- 分布式架构:Debezium 本身是分布式架构,基于 Apache Kafka 实现,可在大规模集群中处理高并发的数据变更。它可以适应企业级的高数据吞吐量和低延迟需求。
- 无缝的数据库集成:Debezium 支持多种常见的数据库,如 MySQL、PostgreSQL、MongoDB、SQL Server 等,通过配置简单的连接器,Debezium 就能实时捕获这些数据库中的数据变更。
- 持久化历史记录:通过将捕获到的变更写入 Kafka 或其他存储,Debezium 可以持久化数据的历史记录,从而使得下游的应用可以随时重放这些事件,来重建数据库的当前状态或数据流。
- 支持容错:Debezium 支持故障恢复机制,能够在连接中断或节点故障时通过读取 Kafka 中的偏移量来恢复状态,并继续从上一次中断的地方重新捕获变更。
1.1.3、Debezium 的架构
Debezium 架构大致如下:
- 数据库连接器:Debezium 通过专门为每个数据库设计的连接器(Connector)来连接到不同的数据库,并监听其事务日志或 binlog。
- Kafka 作为消息队列:Debezium 通常与 Apache Kafka 配合使用,将捕获到的数据库变更事件发布到 Kafka 的 topic 中。Kafka 充当消息分发系统,将这些事件分发到多个消费者应用程序。
- Kafka Connect:Debezium 的连接器基于 Kafka Connect 框架,Kafka Connect 提供了强大的数据流处理能力,使得数据从源数据库到 Kafka 的流转过程非常高效。
- 事件流消费者:下游的应用程序(如微服务、流处理系统或数据仓库)会订阅 Kafka 中的 topic,来实时消费数据库的变更事件。这些事件可以用于触发业务逻辑、更新缓存或同步数据仓库。
1.1.4、典型使用场景
- 数据库与缓存同步:利用 Debezium 可以将数据库变更实时同步到缓存系统(如 Redis),确保缓存中的数据与数据库保持一致。
- 数据仓库/数据湖的同步:Debezium 可以将数据库的变更同步到数据仓库或数据湖中,以构建实时的数据分析平台。
- 微服务架构的数据同步:在微服务架构中,Debezium 可以通过发布事件的方式,将数据库变更传播到多个微服务,从而实现跨服务的数据同步。
- 审计和数据追踪:通过 Debezium 捕获的数据变更日志,可以用于审计数据库的所有历史变更,方便企业进行数据溯源和监管。
1.1.5、Debezium 的优点
- 实时性:Debezium 能够以低延迟的方式捕获数据库的变化,适合对实时性要求高的场景。
- 高可用性和容错性:基于 Kafka 的高可用性架构,Debezium 具有很好的容错能力,可以在系统故障后自动恢复。
- 扩展性:Debezium 支持分布式部署,可以横向扩展来处理大量的数据库变更数据。
- 事件驱动架构:它允许构建事件驱动的微服务架构,支持复杂的数据同步场景。
1.1.6、Debezium 的缺点
- 数据库负载:由于 Debezium 需要持续读取数据库的事务日志,它可能会对数据库系统产生一定的额外负载,特别是在处理大规模数据变更时。
1.1.7、Debezium 示例
以下是一个使用 Debezium 监控 MySQL 数据库变更并将其发送到 Kafka 的简单示例。
{
"name": "mysql-connector",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnector",
"tasks.max": "1",
"database.hostname": "localhost",
"database.port": "3306",
"database.user": "debezium",
"database.password": "dbz",
"database.server.id": "184054",
"database.server.name": "dbserver1",
"database.whitelist": "inventory",
"database.history.kafka.bootstrap.servers": "localhost:9092",
"database.history.kafka.topic": "dbhistory.inventory"
}
}
这个 JSON 配置定义了一个 Debezium MySQL 连接器,Debezium 将监控 inventory 数据库的所有变更,并将其发布到 Kafka 的 dbhistory.inventory topic 中。
总结
Debezium 是一个强大的 CDC 工具,通过实时捕获数据库的变更,帮助企业在数据集成、数据同步、审计等场景中实现更高效的数据处理和管理。它在大规模分布式系统中广泛应用,特别是与 Kafka 结合使用,提供了一种灵活的事件驱动架构。
1.3、主要优势
- 低延迟:基于数据变更捕获(CDC)的方式,确保数据的实时性。
- 高可靠性:Flink 强大的分布式处理能力保证了数据处理的可靠性和可扩展性。
- 多种数据库支持:Flink CDC 支持 MySQL、PostgreSQL、Oracle 等主流数据库。
2、 环境准备
要使用 Flink CDC,首先需要确保以下环境和依赖的配置:
- Flink 版本:1.17 以上
- JDK 版本:1.8 或以上
- Maven:用来管理项目依赖
在本文中,我们以 MySQL 作为数据源,使用 Flink 进行实时数据捕获和同步。
Maven 项目配置
首先,我们需要在 Maven 项目中配置 Flink 和 Flink CDC 的依赖。
创建 Maven 项目
创建一个标准的 Maven 项目,然后在 pom.xml 中加入 Flink 和 Flink CDC 相关依赖。
2.1、 Maven pom.xml 配置
<properties>
<flink.version>1.17.2</flink.version>
<scala.binary.version>2.12</scala.binary.version>
<flink.cdc.version>2.4.0</flink.cdc.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ververica</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-mysql-cdc</artifactId>
<version>${flink.cdc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Debezium 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.debezium</groupId>
<artifactId>debezium-connector-mysql</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-runtime-web</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-api-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-base</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>*</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-clients</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-streaming-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>*</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.google.code.findbugs</groupId>
<artifactId>jsr305</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>force-shading</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3、Flink CDC 实现代码
接下来我们将展示如何使用 Flink CDC 捕获 MySQL 的数据变更,并同步到 Flink 的流处理中。
3.1、MySQL 环境准备
首先,在 MySQL 中准备一张用于演示的表,假设表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100),
age INT,
email VARCHAR(100),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
向表中插入一些初始数据:
INSERT INTO users (name, age, email) VALUES ('Alice', 25, 'alice@example.com');
INSERT INTO users (name, age, email) VALUES ('Bob', 30, 'bob@example.com');
3.2、实现 Flink CDC 的 Java 代码
import com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.source.MySqlSource;
import com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.table.StartupOptions;
import com.ververica.cdc.debezium.StringDebeziumDeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class FlinkCDC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 Flink 执行环境
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// 配置 MySQL Source
MySqlSource<String> mySqlSource = MySqlSource.<String>builder()
.hostname("localhost")
.port(3306)
.databaseList("flinkcdc") // 数据库名称
.tableList("flinkcdc.users") // 需要捕获变更的表
.username("root")
.password("123456")
.deserializer(new StringDebeziumDeserializationSchema()) // 数据反序列化
.startupOptions(StartupOptions.latest()) // 初始选项
.build();
// 创建数据流
DataStreamSource<String> mySqlSourceStream = env.fromSource(
mySqlSource, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), "MySQL CDC Source");
// 打印变更数据
mySqlSourceStream.print();
// 执行作业
try {
env.execute("Flink CDC Example");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
4、讲解与验证
4.1、StartupOptions源码
/*
* Copyright 2023 Ververica Inc.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.table;
import com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.source.offset.BinlogOffset;
import javax.annotation.Nullable;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Objects;
import static org.apache.flink.util.Preconditions.checkNotNull;
/** Debezium startup options. */
public final class StartupOptions implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public final StartupMode startupMode;
@Nullable public final BinlogOffset binlogOffset;
/**
* Performs an initial snapshot on the monitored database tables upon first startup, and
* continue to read the latest binlog.
*/
public static StartupOptions initial() {
return new StartupOptions(StartupMode.INITIAL, null);
}
/**
* Never to perform snapshot on the monitored database tables upon first startup, just read from
* the beginning of the binlog. This should be used with care, as it is only valid when the
* binlog is guaranteed to contain the entire history of the database.
*/
public static StartupOptions earliest() {
return new StartupOptions(StartupMode.EARLIEST_OFFSET, BinlogOffset.ofEarliest());
}
/**
* Never to perform snapshot on the monitored database tables upon first startup, just read from
* the end of the binlog which means only have the changes since the connector was started.
*/
public static StartupOptions latest() {
return new StartupOptions(StartupMode.LATEST_OFFSET, BinlogOffset.ofLatest());
}
/**
* Never to perform snapshot on the monitored database tables upon first startup, and directly
* read binlog from the specified offset.
*/
public static StartupOptions specificOffset(String specificOffsetFile, long specificOffsetPos) {
return new StartupOptions(
StartupMode.SPECIFIC_OFFSETS,
BinlogOffset.ofBinlogFilePosition(specificOffsetFile, specificOffsetPos));
}
public static StartupOptions specificOffset(String gtidSet) {
return new StartupOptions(StartupMode.SPECIFIC_OFFSETS, BinlogOffset.ofGtidSet(gtidSet));
}
public static StartupOptions specificOffset(BinlogOffset binlogOffset) {
return new StartupOptions(StartupMode.SPECIFIC_OFFSETS, binlogOffset);
}
/**
* Never to perform snapshot on the monitored database tables upon first startup, and directly
* read binlog from the specified timestamp.
*
* <p>The consumer will traverse the binlog from the beginning and ignore change events whose
* timestamp is smaller than the specified timestamp.
*
* @param startupTimestampMillis timestamp for the startup offsets, as milliseconds from epoch.
*/
public static StartupOptions timestamp(long startupTimestampMillis) {
return new StartupOptions(
StartupMode.TIMESTAMP, BinlogOffset.ofTimestampSec(startupTimestampMillis / 1000));
}
private StartupOptions(StartupMode startupMode, BinlogOffset binlogOffset) {
this.startupMode = startupMode;
this.binlogOffset = binlogOffset;
if (startupMode != StartupMode.INITIAL) {
checkNotNull(
binlogOffset, "Binlog offset is required if startup mode is %s", startupMode);
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
StartupOptions that = (StartupOptions) o;
return startupMode == that.startupMode && Objects.equals(binlogOffset, that.binlogOffset);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(startupMode, binlogOffset);
}
}
可以看出StartupOptions一共有如下几种
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| initial | 在首次启动时对监控的数据库表执行初始快照,并继续读取最新的 binlog。 |
| earliest | 在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,仅从 binlog 的开头开始读取。此选项应谨慎使用,因为它仅在确保 binlog 包含数据库的全部历史记录时才有效。 |
| latest | 在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,仅从 binlog 的末尾开始读取,这意味着只读取连接器启动后的变更。 |
| specificOffset(String specificOffsetFile, long specificOffsetPos) | 在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,直接从指定的偏移量开始读取 binlog |
| specificOffset(String gtidSet) | 在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,直接从指定的偏移量开始读取 binlog |
| specificOffset(BinlogOffset binlogOffset) | 在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,直接从指定的偏移量开始读取 binlog |
| timestamp(long startupTimestampMillis) | 在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,直接从指定的偏移量开始读取 binlog。在首次启动时从不对监控的数据库表执行快照,直接从指定的时间戳开始读取 binlog。startupTimestampMillis:用于启动偏移量的时间戳,表示自纪元开始以来的毫秒数。 |
5、可能出现的错误和问题
5.1、NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/flink/connector/base/source/reader/RecordEmitter
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/flink/connector/base/source/reader/RecordEmitter
at org.example.FlinkCDC.main(FlinkCDC.java:17)
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.flink.connector.base.source.reader.RecordEmitter
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:387)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:418)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:355)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:351)
... 1 more
出现这个错误是因为pom文件缺乏如下的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-base</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
5.2、org.apache.flink.table.api.ValidationException: The MySQL server has a timezone offset (0 seconds ahead of UTC)
错误内容如下: org.apache.flink.table.api.ValidationException: The MySQL server has a timezone offset (0 seconds ahead of UTC) which does not match the configured timezone Asia/Shanghai. Specify the right server-time-zone to avoid inconsistencies for time-related fields.
出现这个问题是因为数据库的时区和flink执行的时区对不上的原因导致的 修改下数据库的时区就行 首先查看数据库的时区
SELECT @@global.time_zone, @@session.time_zone;
如果发现结果如下:
| @@global.time_zone | @@session.time_zone |
|---|---|
| SYSTEM | SYSTEM |
都是随系统时间的,那就再去查看下系统的时间是多少? 执行如下命令
date
可以看到具体的时区,如果和当前时间时区不一样,那就执行如下命令重新绑定下
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
最后重启mysql数据库,执行成功。。



评论